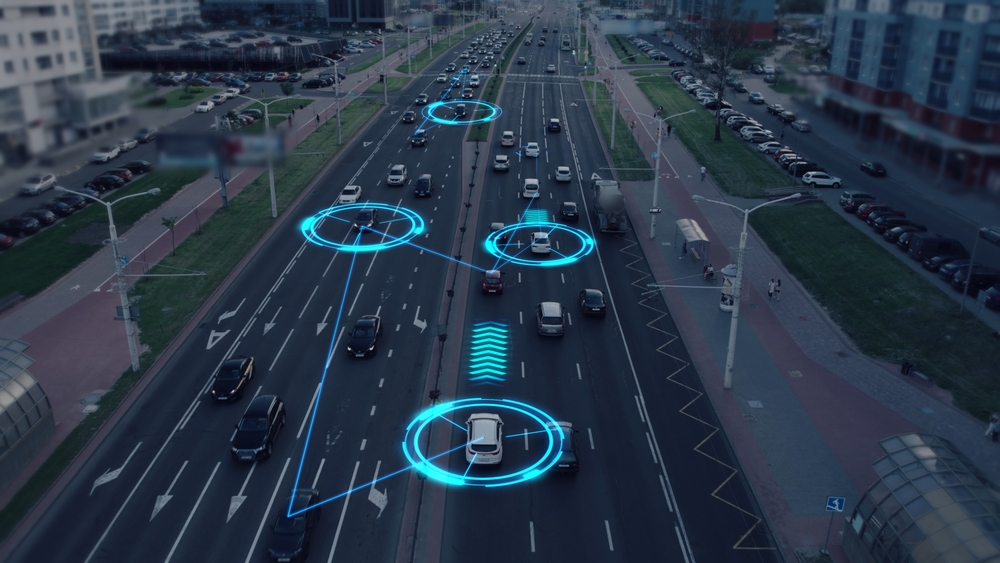
Self-driving cars stand to be the real change in the car industry. Advocates believe they will revolutionize the transportation sector, increasing safety and decreasing congestion and excessive efforts for access. In detail, the book dabbles in any significant technological aspect of one or more self-driving cars, highlighting the background and basic autonomous-navigation components as it takes to mutilate the various aspects such as problems, issues, and futuristics on various scenarios.
Evolution of Self-Driving Cars
The origin of driverless cars dates back to the era just before the twenty-first century that featured advanced driver-assisted systems. There were already features that formed the basis for increasing autonomous complexities, such as Antilock Braking Systems or Electronic Stability Control. It has only been in more recent decades that AI, sensors, and machine learning have pushed driverless car implications to solve problems that required large amounts of judgment or, at the very least, stirred up minor interests.
Core Components of Self-Driving Technology
- Perception Systems: It refers to an area where the vehicle senses its immediate environment using numerous sensors.
- Cameras: High resolution images of the signs, lane markings and obstacles, which are detected by these sensors.
- Lidar: Lightweight detection and ranging, LIDAR makes use of laser pulse to scan the environment and construct a detailed map in 3D view.
- Radar: This sensor determines the distance and speed of surrounding objects; It is very important for adaptive cruise control.
- Ultrasonic Sensors: Useful in short range detection for parking or tight maneuvering.
- Localization and mini-mapping: Accurate localization is fundamental to navigation. The vehicle uses GPS signals along with data from its sensors to pinpoint its precise location; with a high-definition map, it can later gather information that is relevant to road network layout, traffic signs, and other infrastructure.
- Decision-making and planning: Ultimately, driving decisions are made through AI algorithms taking data from the perception systems-that include path planning, obstacle avoidance, and law-abiding driving. Machine-learning models serve to treat a broad variety of driving scenes.
- Control Systems: The declared decisions of driving are realized by applying certain actions-maneuvering acceleration and braking through the vehicle’s wheel system-to ensure smooth as well as safe career.
Levels of Automation
The Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) defines six levels of vehicle automation:
- Level 0: The driver has full control over everything regarding driving.
- Level 1: The driver is assisted in steering or in accelerating/decelerating through systems such as adaptive cruise control.
- Level 2: The systems can steer and accelerate/decelerate under strictly attentive driver control.
- Level 3: The car can do all driving tasks on its own, but in specific cases, it needs intervention from humans.
- Level 4: The vehicle is capable of all necessary driving functions without any human interaction under certain circumstances.
- Level 5: The car drives itself faultlessly under all circumstances without the involvement of a human driver.
Current Applications and Developments
- The base end for self-driving technology publication has since moved into the company’s newsroom.
- Waymo is a slice of Alphabet Inc. The untampered endeavor is having wade trials for absolutely self-racing automobiles in Phoenix and San Francisco, and is giving rides within a predetermined area, without safety drivers.
- Tesla: All the goodies are set in FSD (Full Self-Driving) offered by Tesla. There are functions such as Highway driving and lane changes included. Of course, the one drinking bourbon should be paying attention to driving, and not loafing one-off when you are supposed to be in control; this is essentially Level 2 self-drive.
- Apollo Go by Baidu: Apollo started with 400 robo-taxis in Wuhan, China, with a roadmap plan for achieving 1,000 vehicles. Thus, Baidu is setting industry standards for service hailing-related autonomous driving within urban areas.
Challenges Facing Self-Driving Cars
- Even as the latest technologies struggle to realize their potential, they are confronted and disrupted by difficulties that discourage the widespread adoption of these:
- Safety and Reliability: The performance of self-driving vehicles has to be particularly safe against any unforeseen and different challenges that may cross its way. Knowing how to handle these “edge cases” or perhaps rare cases-and given the fact that the vehicle might have never faced them during its training-is an even trickier issue.
- Regulatory and Legal Frameworks: The establishment of a tangible regulatory framework is necessary to incorporate autonomous vehicles within common public transit activities. Such a regulatory framework will have to include legislation for liability, insurance, and general ethical considerations.
- As per public survey, this is generally crucial to look forward to obtaining public support. It is advised that public education is focused and transparent for the acceptance of some of these technologies, which were not just highlighted in surveys.
Future Prospects
- The self-driving cars have several end routes, with personal transportation being only that, and not its zenith.
- This includes diminished road accident rates: faulty driving is the cause for up to three-quarters of crashed cases which will be brought down considerably by AVs.
- Ease of Movement: The elderly or the disabled will find their mobility increasing over a completely new level.
- Environmental benefits: With no traffic jams, one expects fuel consumption to decrease significantly together with CO2-emission levels.
- Socio-economic impacts: The self-driving technology sector is expected to increase to £42 billion by 2035 only in the UK, creating thousands of jobs for skilled workers and hence fostering economic growth.
Conclusion
There’s a worldwide anticipation for automotive technology, with self-driving cars merely touching the tip of the iceberg. Along with numerous challenges, the road has to be paved through research, innovations in technology, and partnerships among stakeholders from different industries, regulators, and the public itself, toward a future in which human drivers and autonomous cars shall seamlessly share roads in daily society. A central aspect of realizing the potential of the transformer technology involves emphasizing safety, ethical considerations, and transport only.
Also Read : The rise of EVs: Sustainable future